


- Where is the worlds population distrubuted?
1A. - Describe the regions of where population is clustered and where it is sparse.
- The four major regions where population is clustered are East Asia, South Asia, Europe and Southern Asia. Clusters can be found can form major cities and they usually start along waterways that provide a necessary resource to survive. Places are usually sparse is it is too dry, too wet, too cold, too mountainous places with lots of unfarmable land.
1B. - Define and give examples of three types of density used in population geography.
- Arithmetic - Most popular kind that geographers use; the total number of objects in an area.
- Physiological- The number of people supported by a unit area of arable land this helps geographers understand how much food is needed to sortp the number of people living there.
- Agricultural- The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land; developed countries have lower agricultural densities because of technology
- Why is global population increasing?
2A. Demonstrate how to measure population growth through the natural increase rate using any country.
- You demonstrate population growth through natural increase rate you take the crude birth rate and subtract the crude death rate to find the population growth.Take Denmark for example thier CBR is 10 live briths for 1,000people (in 2014) and thier CDR is 9 deaths (in 2014) now subtrace them and you get a natural groth rate of 1 child.
2B. Demonstrate how to measure birth and death through CBR and CBD using a different nations than you chose for task 2a.
- Hungary's CBR is 9 in 2014 and the CDR is 13 in 2014 this means in 2014 alwas all of the live births in Hungary died.
2C. Describe how to read a population pyramid. Provide an example of a population pyramid for a developing nation and a developed nation.
- First look at the bottom of the model if it has a wide base and a narrow top that means that it it proboly from a deovevoping conuty, if it has a generaly normal withall the way thew then it might be from a place it stage 4, if the base is narrow and the top is wider then the population is at stage 5 where the population has advanced so much it is pointless to have kids.

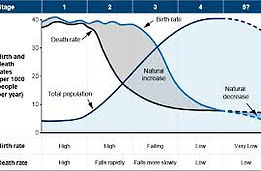

-Why does population growth vary among regions?
3A. Provide an example of the demographic transition model. Describe a country in the modern purled that resides each stage.
- The demomgraphic transition model Is an model that shows the population and what that population would be as a stage.
3B. Identify two approaches to reducing birth rates.
- Give women a high social statis and education oppotunities and provide family planning programs.
3C. Describe Malthus’s argument about the relationship between population and resources. make sure to provide a visual reference.
Malthuse said that the world's population would continue to grow until there is no more of the worlds resourses left and then the population startes to fall vary quickly.
3D. Describe the possible stage five of the DTM. Which countries in the modern world may be in this fifth stage.
- Stage 1-Ethiopa
- Stage 2- India, Boivia
- Stage 3- China
-Stage 4- Alstralia ,Canida, USA
- Stage 5 - United Kindom
Why do regions face health threats?
4A. Describe the diffusion of AIDS
AIDS is a disease that weakenss the innume system and makes the body vary subcepibul to other illness.
4B. Describe the reasons for variations in health between developed and developing countries.
Developed countries have the medican and tecnology to fight agest illnesses and even prevent them. Developing countries don't have the the same advancements as developed countries.
